|
 |
The Student t distribution statistics are used to assess
the statistical significance of ranking of protein structure modeling methods.
Four different measures are used to assess the quality of a model:
- Fold accuracy.
Percentage of equivalent C-alpha positions (within 3.5 Angstroms) between the optimally superimposed target and model structures.
- Alignment accuracy.
Percentage of equivalent C-alpha positions (within 3.5 Angstroms) between the alignment based superimposition of target and model structures.
- C-alpha global RMSD.
C-alpha atoms RMSD after superimposition of the model and the target structures.
- Model coverage.
Percentage of modeled residues with respect to target length.
Ranking protocol:
For each method X, a temporary ranking was constructed
for it and for all other methods Y with which it shared at
least one model, using the average model quality differences.
The final ranking list was obtained by averaging
the rank positions in all the temporary ranking lists.
The ranking results and its significance are tabulated as follows:
Red background = Significant difference between two methods
Information provided:
Average difference ± Standard Deviation [Number of common models between groups] |
Green background = No significant difference found between two methods
Information provided:
Average difference ± Standard Deviation [Number of extra common models needed for significant distinction]*
(*) For large sample sizes (n > 100) the t-distribution tends
to the normal distribution. The calculation of the number of models
required to make a significant difference (wherever applicable) is
hence always set to 'infinity' (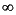 )
in cases where this number exceeds 100. )
in cases where this number exceeds 100.
|
Note that the results shown in the ranking page contain only pairwise comparisons between all methods in Eva-CM.
Other general analysis in the results page contain results for all models submitted
to Eva-CM.
|
|
|