 Serine Proteases Part 2
Serine Proteases Part 2
 Index
to Course Material
Index
to Course Material Index
to Section 12
Index
to Section 12 Enzymes
Index;
Enzymes
Index;  Part
1
Part
1 Part
3
Part
3
Tertiary structure of the Chymotrypsin Superfamily
The homologous enzymes chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastase consist
of two similar domains, each of which is a six-stranded antiparallel beta
barrel (for a description of this type of fold, refer to the page in
Section
10). Some of the loops between the strands include helical sections.
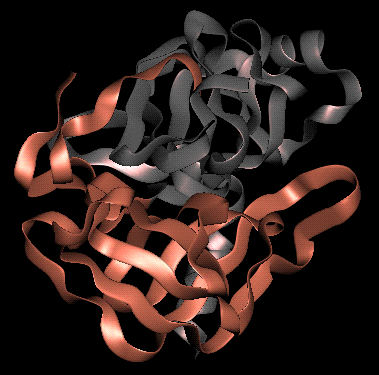
The two domains are different colours
Recall that chymotrypsin consists of three chains, due to several cleavages
of the initial zymogen polypeptide. These chains are joined by disulphide
bonds. Trypsin on the other hand is a single chain, as the zymogen is activated
by removal of the first six residues. There is a marked difference between
the conformation of four regions (called the
activation domain )
of the trypsin polypeptide compared to its zymogen (Stroud et al,
1977; Huber and Bode, 1978).
Substrates of serine proteases
Proteases are all hydrolases - i.e. they cleave bonds by hydrolysis.
(The hydrolases
entry of the Enzyme
Structures Database, Roman Laskowski and Andrew Wallace Biomolecular
Structure and Modelling Group, University College London). Proteases
are so named because they hydrolyse peptide bonds; however the chymotrypsin
superfamily of serine proteases also cleave ester bonds of certain
synthetic substrates.
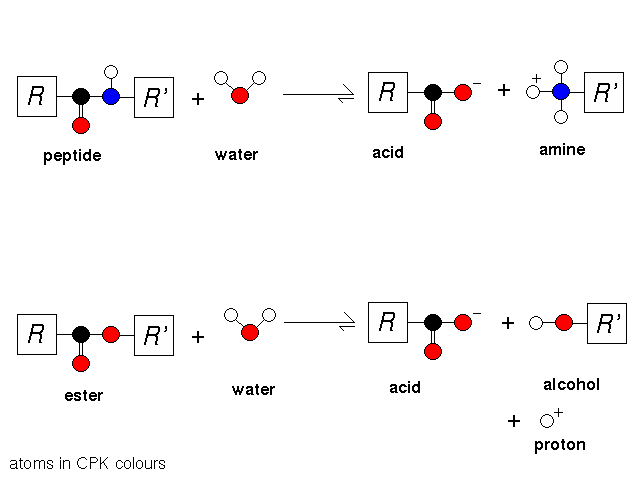
Although the serine proteases have no absolute
specificity, they have strong preferences for the peptide bonds adjacent
to specific amino acid residues. The important side chain is the one preceding
the scissile bond (i.e. the one which is cleaved) in the sequence,
that is, R in the above diagram.
-
Trypsin prefers the positively charged Lys and Arg side chains
-
Chymotrypsin prefers large hydrophobic side chains (Phe, Tyr, Trp)
-
Elastase prefers small hydrophobic side chains such as Ala
This specificity depends on the size and nature of the three residues which
form the specificity pocket, described subsequently.
 Index
to Course Material
Index
to Course Material Index
to Section 12
Index
to Section 12 Enzymes
Index;
Enzymes
Index;  Part
1
Part
1 Part
3
Part
3
Last updated 10th Jul '96
 Serine Proteases Part 2
Serine Proteases Part 2![]() Index
to Course Material
Index
to Course Material![]() Index
to Section 12
Index
to Section 12![]() Enzymes
Index;
Enzymes
Index; ![]() Part
1
Part
1![]() Part
3
Part
3

