| PDB - EBI | Protein Data Bank (EBI) | EXAMPLE
(a PDB coordinates file) |
| PDB - RCSB | Protein Data Bank (RCSB) | |
| PDBsum
(very useful) |
Summaries and structural analyses of PDB data files (UCL, UK) | EXAMPLE |
| OCA | PDB advanced browser (EBI) | EXAMPLE |
| EC->PDB | Enzyme Structures deposited in PDB (UCL, UK) | EXAMPLE |
| Prosite->PDB | PROSITE patterns in PDB entries (UCL, UK) | EXAMPLE |
| Ligands->PDB | List of ligands bound to PDB srtuctures (UCL, UK) | EXAMPLE |
| NDB | The Nucleic Acid Database Project (UK) (Nucleic Acid Structures) | EXAMPLE |
| PQS | Protein Quaternary Structure Database Searches at the EBI | EXAMPLE |
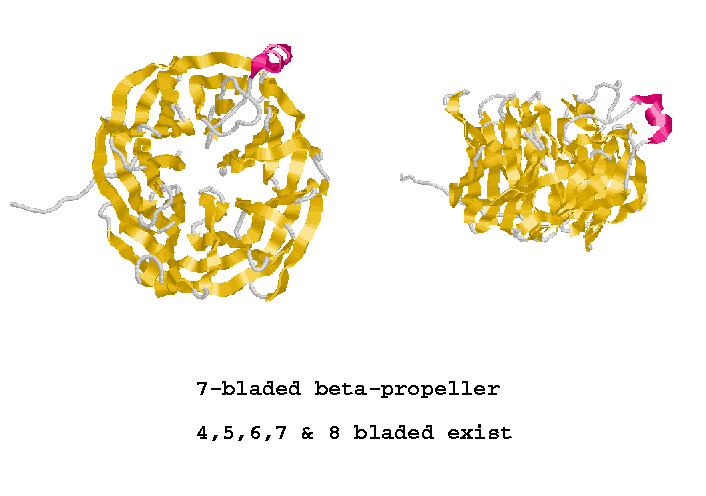
| SCOP | Structural Classification of Proteins (MRC-LMB, UK).
The SCOP database, created by manual inspection and abetted by a battery of automated methods, aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive description of the structural and evolutionary relationships between all proteins whose structure is known. As such, it provides a broad survey of all known protein folds, detailed information about the close relatives of any particular protein, and a framework for future research and classification. |
EXAMPLE |
| CATH | CATH Protein Structure Classification (UCL-BSM, UK).
CATH is a hierarchical classification of protein domain structures, which clusters proteins at four major levels, Class(C), Architecture(A), topology(T) and homologous superfamily (H). Class, derived from secondary structure content, is assigned for more than 90% of protein structures automatically. Architecture, which describes the gross orientation of secondary structures, independent of connectivities, is currently assigned manually. The topology level clusters structures according to their toplogical connections and numbers of secondary structures. The homologous superfamilies cluster proteins with highly similar structures and functions. The assignments of structures to topology families and homologous superfamilies are made by sequence and structure comparisons. |
EXAMPLE |
| FSSP | Fold classification based on Structure-Structure alignment of Proteins
(FSSP) (EBI)
FSSP stands for Fold classification based on Structure-Structure alignment of Proteins. Structure alignments are performed automatically using the Dali program. All protein chains from the Protein Data Bank which are longer than 30 residues are included. The chains are divided into a representative set and sequence homologs of structures in the representative set. Sequence homologs have more than 25 % sequence identity, and the represenative set contains no pair of such sequence homologs. An all-against-all structure comparison is performed on the representative set. The resulting alignments are reported in the FSSP entries for individual chains. In addition, FSSP entries include the structure alignments of the search structure with its sequence homologs. |
EXAMPLE |
| DaliDD | Dali Domain Dictionary: structural classification of protein domains
(EBI)
The Dali Domain Dictionary is a structural classification of protein domains. Domains are delineated automatically optimising topological recurrence between large, compact units in the known protein structures. The pairwise structural relationships define an abstract fold space. The overall distribution of folds in this fold space is shown in eigenvector projections onto a plane. Similar structures are clustered hierarchically into fold classes, or structural neighbourhoods, at four different radii. We visualize sequence and structure conservation mapped onto a central member of each fold class or subclass. The fold classes are indexed in order of decreasing population of sequence-unique protein families. |
EXAMPLE |
|
|
|
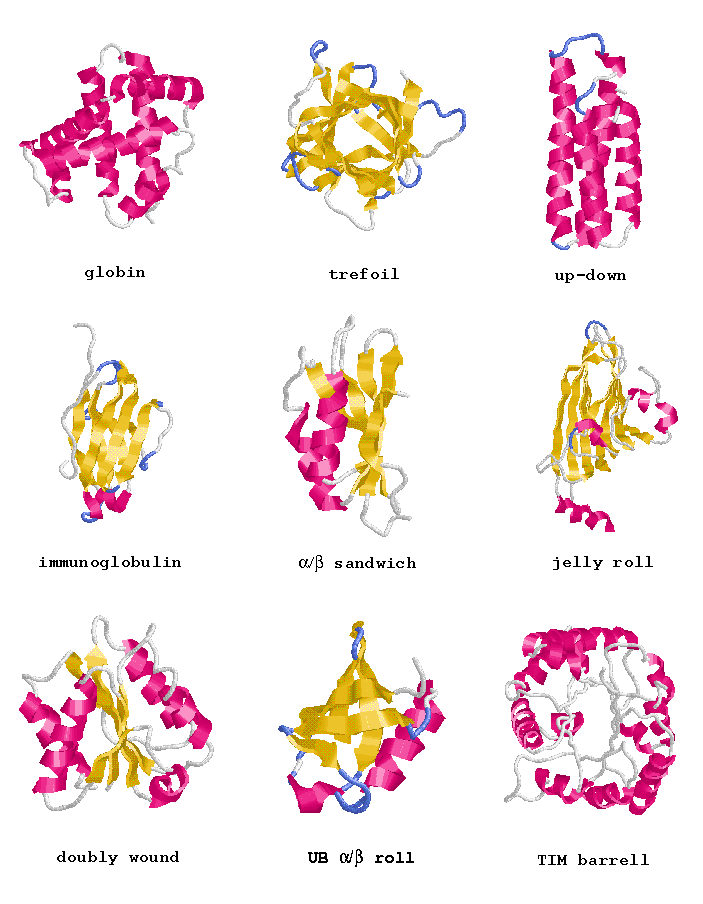 |
 |